This class represents a search being performed by the user. It allows you to get more information about the context of the search, as well as narrowing down the search results with additional conditions. |
This search handler adds an extra query condition to the SearchContext, in order to only show Contacts related to the selected Account.
global class MyContactSearch extends B25.SearchHandler {
global override B25.SearchResultCollection getSearchResults(B25.SearchContext searchContext) {
Id accountId = searchContext.getForm().getReservation().B25__Account__c;
if (accountId != null) {
searchContext.addCondition('AND Account = \'' + accountId + '\'');
}
return searchContext.getDefaultResults();
}
} |
String getSearchTerm() |
Returns the search term that the user has typed.
Return value: String
B25.SearchResultCollection getDefaultResults() |
Returns a Collection wrapping the results that would be generated by GoMeddo, modified by any conditions defined (also see addCondition).
To access the individual results, call getResults() on the Collection.
Return value: B25.SearchResult.Collection
B25.Form getForm() |
Returns the Form object that the user has performed the search on. This can be useful to get more information about the other fields that have been filled in on the reservation, using the Form.getReservation method.
Return value: B25.Form
List<String> getConditions() |
Returns the conditions that have already been defined. These will narrow down the search results returned by getDefaultResults(). As this is a reference to the actual list, you can still manipulate this list (such as adding or removing entries) before calling getDefaultResults().
Return value: List<String>
void addCondition(String condition) |
Adds a condition to narrow down the search results returned by getDefaultResults(). Functionally identical to calling getConditions().add(condition).
Dynamic references to parameters (i.e. ‘Account = :accountId’) will not work. Make sure to escape ids in the following way:
addCondition('Account = \'' + accountId + '\''); |
Parameters:
Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
condition | String | The condition that you want to add. |
List<String> getSearchFields() |
Returns the fields that will be queried for the search term.
Return value: List<String>
void addSearchField(String fieldName) |
Adds a field to be queried for the search term. For example, if you also want to search for contacts by phone number, do the following:
searchContext.addSearchField('HomePhone');
searchContext.addSearchField('MobilePhone'); |
If the user performing the search has no access to any of these fields, they are ignored. So if the user has no access to the MobilePhone field in the example above, only the HomePhone field is searched.
If the user performing the search has no access to any of these fields, they are ignored. So if the user has no access to the MobilePhone field in the example above, only the HomePhone field is searched.
You can also search for fields on related records. For example, if you also want to search for contacts by account name, do the following:
searchContext.addSearchField('Account.Name'); |
Parameters:
Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
fieldName | String | The API name of a field that you want to be searched. |
void setLabelTemplate(String template, List<String> mergeFields) |
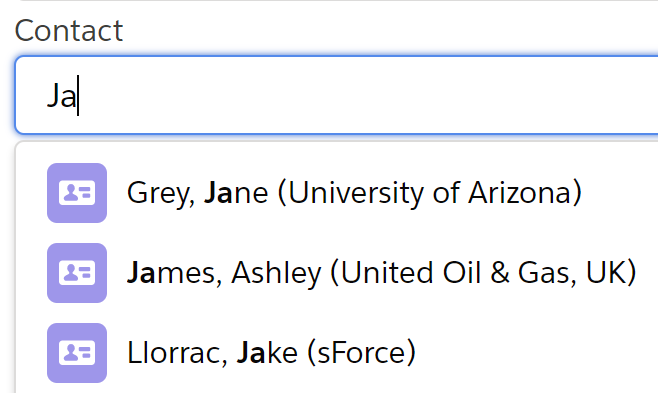
This method lets you define what the label of each search result should be, based on one or more merge fields. For example, if you want to display your contact labels like this: LastName, FirstName (AccountName), you would do the following:
searchContext.setLabelTemplate('{0}, {1} ({2})', new List<String>{'LastName', 'FirstName', 'Account.Name'}); |
The above would result in an output like this:
If the user performing the search has no access to any of these fields, they are replaced with an empty string.
If the user performing the search has no access to any of these fields, they are replaced with an empty string.
By default (so if you would never call this method) only the record name is displayed as the label. This is the same as doing the following:
searchContext.setLabelTemplate('{0}', new List<String>{'Name'}); |
Parameters:
Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
template | String | A string containing numbered placeholders which will be replaced with actual values in the final result. |
mergeFields | List<String> | An ordered list of merge field API names. These will replace the matching placeholders in the template with each record’s actual values. |
void setMetaTemplate(String template, List<String> mergeFields) |
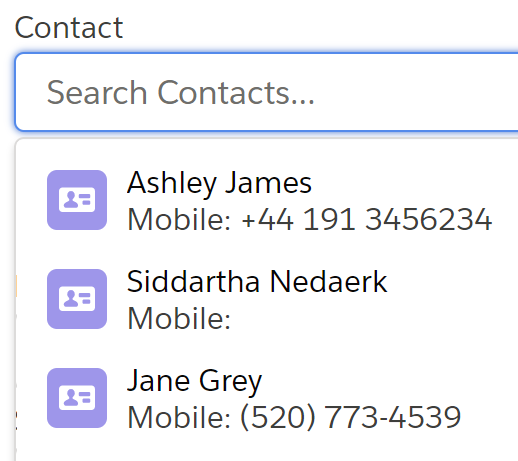
Similar to the above method setLabelTemplate, except this method lets you define the meta text instead of the label. The meta text is displayed under the label, and can provide more information about a record. For example, you could use it to display a contacts phone number:
searchContext.setMetaTemplate('Mobile: {0}', new List<String>{'MobilePhone'}); |
The above would result in an output like this:
If the user performing the search has no access to any of these fields, they are replaced with an empty string.
If the user performing the search has no access to any of these fields, they are replaced with an empty string.
Parameters:
Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
template | String | A string containing numbered placeholders which will be replaced with actual values in the final result. |
mergeFields | List<String> | An ordered list of merge field API names. These will replace the matching placeholders in the template with each record’s actual values. |
void setDefaultIcon(String icon) |
Sets the icons for the results generated through this context. You can use icons from this page: https://www.lightningdesignsystem.com/icons/ , except for the icons in the Action category. Reference icons by combining the category and the icon name, with a colon in between. For example, 'standard:contact' will give you the contact icon from the Standard category.
Return value: B25.SearchResult
searchContext.setDefaultIcon('utility:activity') |
Parameters:
Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
icon | String | The name of the icon. |
void setOrderBy(String orderField, String sortOrder) |
Used to override the sorting mechanism for the results generated through this context.
For example, searchContext.setOrderBy('Email', 'ASC NULLS LAST') will alphabetically sort the returned records by the Email field on the object, with the records that contain no email address put at the bottom.
Possible values for sort order include:
ASC NULLS FIRST
ASC NULLS LAST
ASC
DESC NULLS FIRST
DESC NULLS LAST
DESC
Return value: B25.SearchResult
searchContext.setOrderBy('Email', 'ASC NULLS LAST') |
Parameters:
Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
orderField | String | The field name that will be used to sort the results. |
sortOrder | String | The sorting clause that will be applied to the results. |
void setOrderBy(List<String> orderFields, List<String> sortOrders) |
Used to override the sorting mechanism for the results generated through this context. Results will be ordered by the entries in orderFields and sortOrder, starting with the first in each of the two lists.
Take the following example:
List<String> orderFields = new List<String>{'FirstName', 'LastName'};
List<String> sortOrders = new List<String>{'ASC NULLS LAST', 'DESC'};
searchContext.setOrderBy(orderFields, sortOrders); |
This will alphabetically sort the returned records by the FirstName field on the object, with the records that contain no FirstName put at the bottom.
Then, for each record with a duplicate FirstName, the records will be ordered by how recently they were created.
Note that the number of ordering fields must match the number of sort order clauses provided.
Possible values for sort order include:
ASC NULLS FIRST
ASC NULLS LAST
ASC
DESC NULLS FIRST
DESC NULLS LAST
DESC
Return value: B25.SearchResult
searchContext.setOrderBy(new List<String>{'FirstName', 'LastName'}, new List<String>{'ASC NULLS LAST', 'DESC'}) |
Parameters:
Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
orderFields | List<String> | The field names that will be used to sort the results. |
sortOrders | List<String> | The sorting clauses that will be applied to the results. |